In December 2024, the European Commission launched an investigation following “serious indications that foreign actors interfered in the Romanian presidential elections using TikTok.” The elections have been described as a “first big test” for “Europe’s digital police” and the Digital Services Act.
In January 2025 a group of us met at the Digital Methods Winter School at the University of Amsterdam to explore how TikTok was used during and after the elections.
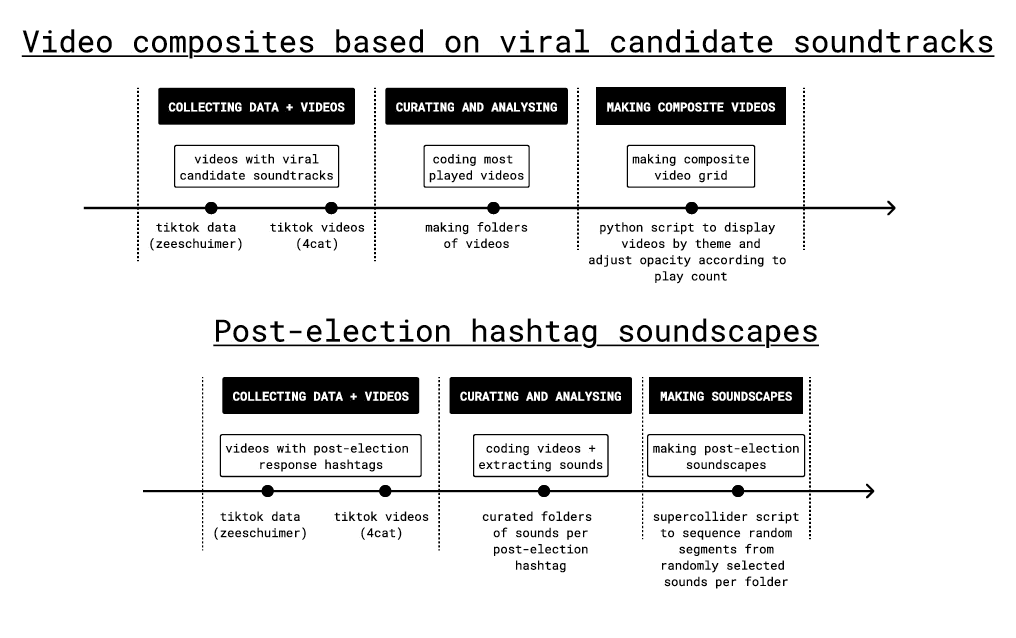
We explored ways of playing back election TikTok video collections to understand what happened.
We experimented with formats for retrospective display – drawing inspiration from creative coding, algorithmic composition, multiperspective live action replays, and the aesthetics of forensic reconstruction.
Following research on visual methods for studying folders of images (Niederer and Colombo, 2024; Colombo, Bounegru & Gray, 2023) and analytical metapicturing (Rogers, 2021), these formats display multiple videos simultaneously to surface patterns and resonances across them.
Beyond evaluating informational content, group replay formats can also highlight the everyday situations, aesthetics and affective dimensions of election TikTok videos – from sexualised lip-syncing to rousing AI anthems, sponsored micro-influencer testimonials to post-communist nationalist nostalgia.
We explored two approaches for critically replaying Romanian election videos: making video composites based on viral candidate soundtracks, and making post-election hashtag soundscapes. For the former we used a Python script to display videos by theme and adjust opacity according to play count. For the latter we used soundscaping scripts developed as part of the Forestscapes project.
For the video composites we used as case studies two viral soundtracks associated with ultranationalist Călin Georgescu and the centre-right, pro-EU, Save Romania Union candidate Elena Lasconi.

Our preliminary findings indicate that successful pro-Georgescu propaganda using the “SustinCalin Georgescu” soundtrack relies on memetic imitation of the message and affective resonances of the song. TikTok influencers and everyday users translate these into popular formats such as lipsyncs and ASMR videos effectively blending textual, visual, and audio elements.
Gender, sexuality and race are prominent themes in the most engaged with propagandist videos for both campaigns. In pro-Georgescu content, popular endorsement videos often feature white women in either sexualised roles or domestic family settings. Homophobic and transphobic videos with male characters in dresses parody the opponent’s and her party’s association with LGBTQ issues, fuelling the audience’s strong emotions towards minoritised groups.
For the “Hai Lasconi la Putere” propagandistic song, the most significant finding is its successful appropriation for counter-propaganda to spread racist, sexist, homophobic, and transphobic content targeting minoritised groups. These videos do not only target Lasconi but more worryingly these groups themselves, amplifying fears and prejudices, as often reflected in the comments.
The second technique we explored was post-election hashtag soundscaping. We examined hashtags such as: #anularealegeri, #aparamdemocratia, #calingeorgescupresedinte, #cg, #cinetaceestecomplice #demisiaccr, #demisiaiohanis, #lovituradestat, #romaniatacuta, #romaniavanduta, #stegarul, #stegaruldac and #votfurat.
For example, in the #stegaruldac soundscape the simultaneous replay of TikTok video soundtracks associated with this hashtag enables a synthetic mode of attending not only to the content of propaganda but also to the various settings in which propaganda unfolds in everyday life (e.g. in the home and on the street) as well as associated affective atmospheres.
You can explore our project poster and some of our video composites and soundscapes here.