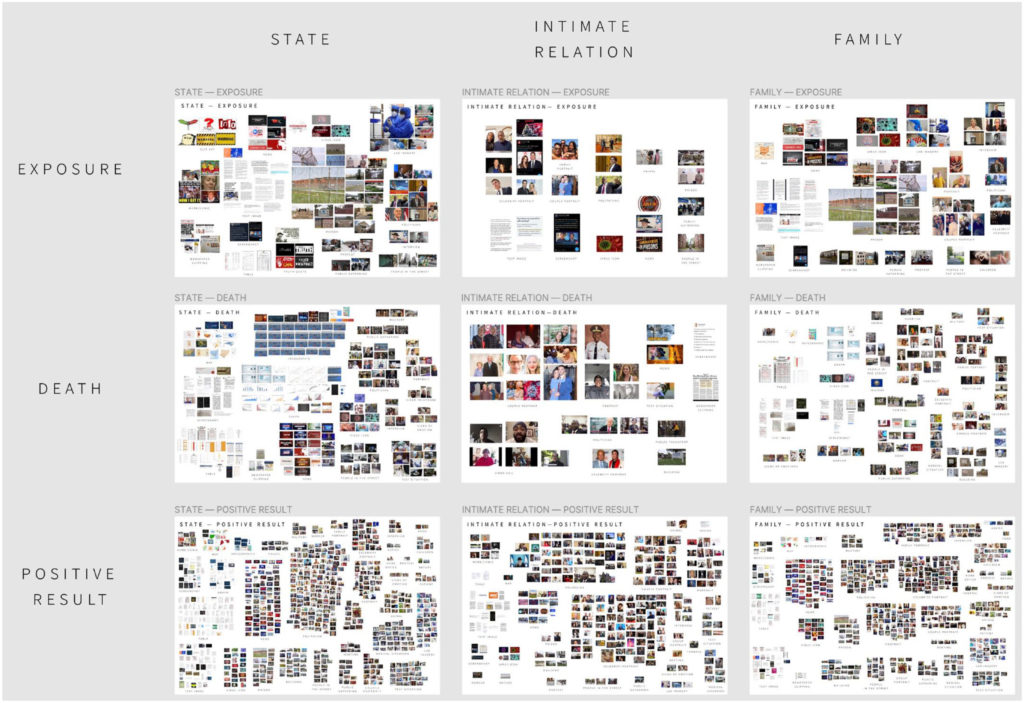
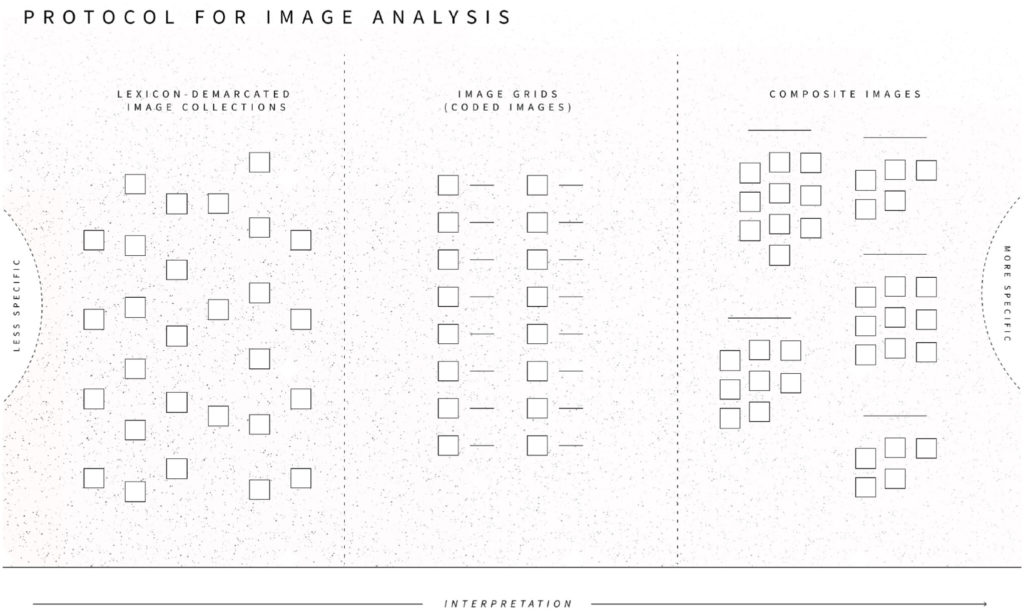
An article on “The platformisation of software development: Connective coding and platform vernaculars on GitHub” by Liliana Bounegru has just been published in Convergence: The International Journal of Research into New Media Technologies.
The article is accompanied by a set of free tools for researching Github co-developed by Liliana with the Digital Methods Initiative – including to:
- Extract the meta-data of organizations on Github
- Extract the meta-data of Github repositories
- Scrape Github for forks of projects
- Scrape Github for user interactions and user to repository relations
- Extract meta-data about users on Github
- Find out which users contributed source code to Github repositories
The article is available open access here. The abstract is copied below.
This article contributes to recent scholarship on platform, software and media studies by critically engaging with the ‘social coding’ platform GitHub, one of the most prominent actors in the online proprietary and F/OSS (free and/or open-source software) code hosting space. It examines the platformisation of software and project development on GitHub by combining institutional and cultural analysis. The institutional analysis focuses on critically examining the platform from a material-economic perspective to understand how it configures contemporary software and project development work. It proposes the concept of ‘connective coding’ to characterise how software intermediaries such as GitHub configure, valorise and capitalise on public repositories, developer and organisation profiles. This institutional perspective is complemented by a case study analysing cultural practices mediated by the platform. The case study examines the platform vernaculars of news media and journalism initiatives highlighted by Source, a key publication in the newsroom software development space, and how GitHub modulates visibility in this space. It finds that the high-visibility platform vernacular of this news media and journalism space is dominated by a mix of established actors such as the New York Times, the Guardian and Bloomberg, as well as more recent actors and initiatives such as ProPublica and Document Cloud. This high-visibility news media and journalism platform vernacular is characterised by multiple F/OSS and F/OSS-inspired practices and styles. Finally, by contrast, low-visibility public repositories in this space may be seen as indicative of GitHub’s role in facilitating various kinds of ‘post-F/OSS’ software development cultures.