An article on “Testing and Not Testing for Coronavirus on Twitter: Surfacing Testing Situations Across Scales With Interpretative Methods” has just been published in Social Media + Society, co-authored by Noortje Marres, Gabriele Colombo, Liliana Bounegru, Jonathan W. Y. Gray, Carolin Gerlitz and James Tripp, building on a series of workshops in Warwick, Amsterdam, St Gallen and Siegen.
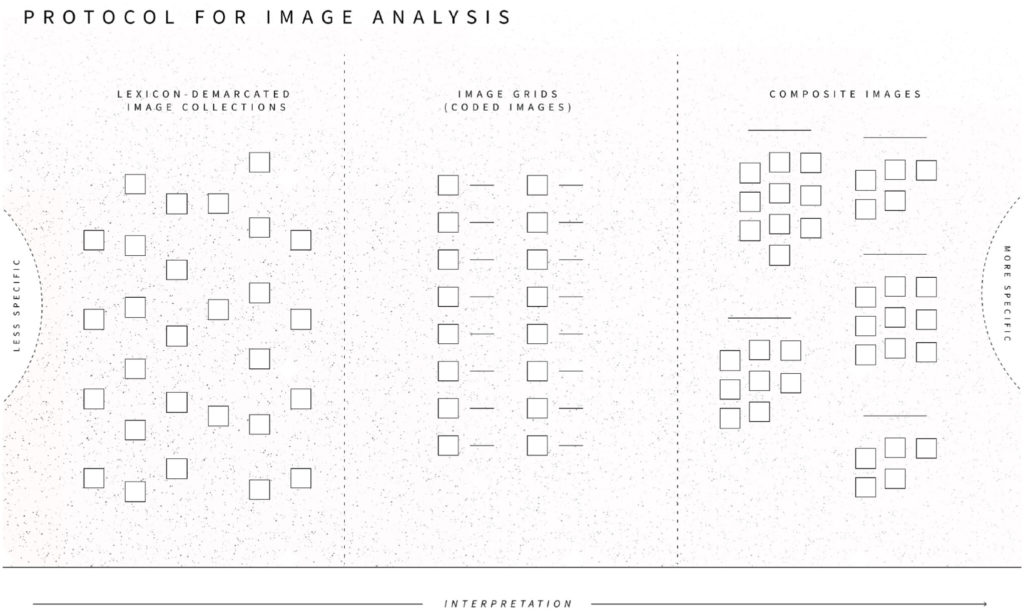
The article explores testing situations – moments in which it is no longer possible to go on in the usual way – across scales during the COVID-19 pandemic through interpretive querying and sub-setting of Twitter data (“data teasing”), together with situational image analysis.
The full text is available open access here. Further details and links can be found at this project page. The abstract and reference are copied below.
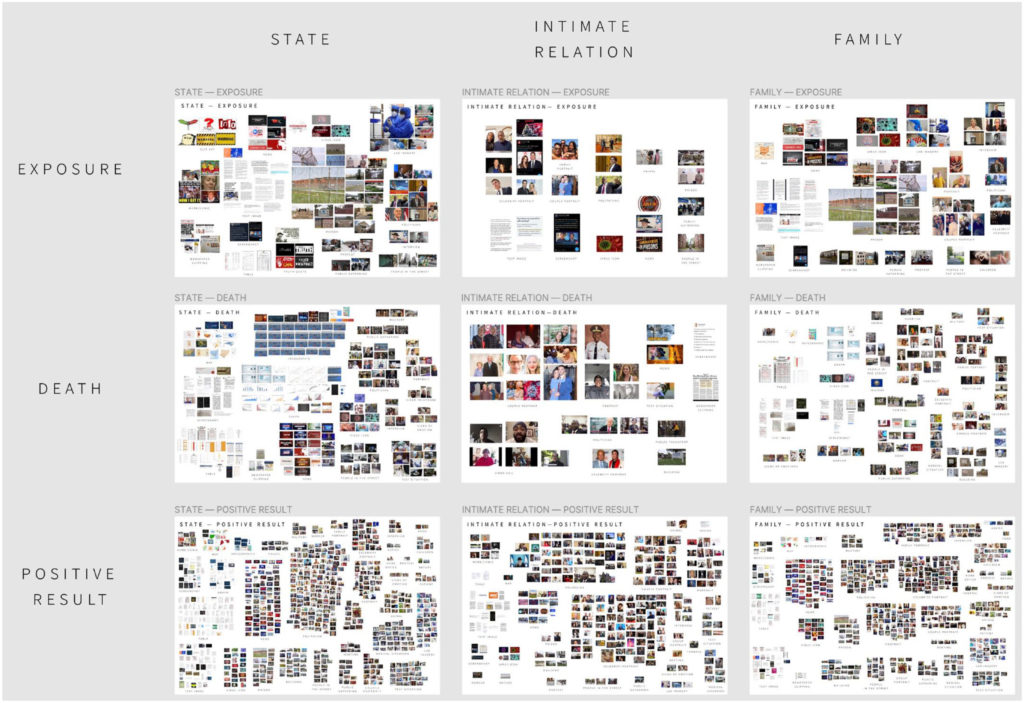
How was testing—and not testing—for coronavirus articulated as a testing situation on social media in the Spring of 2020? Our study examines everyday situations of Covid-19 testing by analyzing a large corpus of Twitter data collected during the first 2 months of the pandemic. Adopting a sociological definition of testing situations, as moments in which it is no longer possible to go on in the usual way, we show how social media analysis can be used to surface a range of such situations across scales, from the individual to the societal. Practicing a form of large-scale data exploration we call “interpretative querying” within the framework of situational analysis, we delineated two types of coronavirus testing situations: those involving locations of testing and those involving relations. Using lexicon analysis and composite image analysis, we then determined what composes the two types of testing situations on Twitter during the relevant period. Our analysis shows that contrary to the focus on individual responsibility in UK government discourse on Covid-19 testing, English-language Twitter reporting on coronavirus testing at the time thematized collective relations. By a variety of means, including in-memoriam portraits and infographics, this discourse rendered explicit challenges to societal relations and arrangements arising from situations of testing and not testing for Covid-19 and highlighted the multifaceted ways in which situations of corona testing amplified asymmetrical distributions of harms and benefits between different social groupings, and between citizens and state, during the first months of the pandemic.
Marres, N., Colombo, G., Bounegru, L., Gray, J. W. Y., Gerlitz, C., & Tripp, J. (2023). Testing and Not Testing for Coronavirus on Twitter: Surfacing Testing Situations Across Scales With Interpretative Methods. Social Media + Society, 9(3). https://doi.org/10.1177/20563051231196538